

These general purpose registers are used to hold data like any other registers.Apart from accumulator 8085 consists of six special types of registers called General Purpose Registers.This register is used by control systems to hold operand, intermediate operand, and address of memory and I/O devices temporarily.Temporary register is an 8-bit register.This temporary register can only be accessed by the microprocessor and it is completely inaccessible to programmers.of ones this flag is reset.ĬPU registers of INTEL 8085 are as follows: If MSB bit =0 then the number is positive, else it is negative.If an operation performed in ALU results 0value of entire 8-bits then zero flag is set, else it resets.If an operation performed in ALU generates the carry from lower nibble (D0 to D3) to upper nibble (D4 to D7) AC flag is set, else it resets.If an operation performed in ALU generates the carry from D7 to next stage then CY flag is set, else it is reset.Note: X represent unspecified bits termed as "don't care". They are called Zero (Z), Carry (CY), Sign (S), Parity (P), and Auxiliary Carry (AC) flags.Once an operation is performed by ALU the result is transferred on internal data bus and status of result will be stored in flip flops.Flag register is a group of flip flops used to give status of different operations result.ALU can store immediate result in temporary register. It is also called as operand register (8 bit).The user can access this register by giving appropriate instructions (commands).

The result of an operation is stored in the accumulator.This register is used to store 8-bit data and to perform arithmetic and logical operations.The accumulator is an 8-bit register that is a part of arithmetic/logic unit (ALU).It is one of the general purpose register of microprocessor also called as A register.of flags either to indicate conditions arising after last ALU operation or to control certain operations. Status Register: Also known as flag register. The result of operation is again stored into accumulator. Shifter: It performs logical operations like rotate left, rotate right, etc. The result of operation is stored into accumulator. Figure shown below shows some functional sections of ALU:Īdder: It performs arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, increment, decrement, etc.
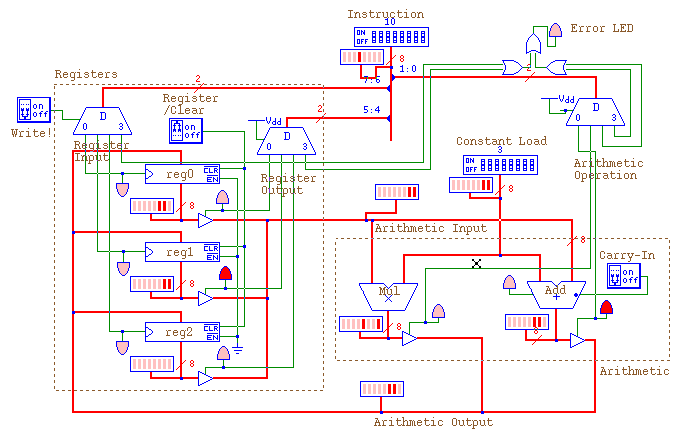
INSTRUCTION DECODER LOGICWORKS 5 SERIAL
The internal architecture of 8085 includes the ALU, timing and control unit, instruction register and decoder, register array, interrupt control and serial I/O control.ĬPU comprises of ALU, timing and control unit, instruction register and decoder, register array, interrupt control and serial I/O control.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
